any infection that spreads from animals to people is referred to by what term?
Introduction [edit | edit source]

Infectious diseases are spread by either bacterial or viral agents and are ever-present in society. Usually infected cases are present in numbers below an expected thresholdA but every once in a while there may exist an outbreak, a new strain or a new illness that has a significant impact at either a local or global level[1]. The spread and rate of new cases tin can exist classified every bit[ane]:
- Owned - describes a disease that is present permanently in a region or population
- Epidemic - is an outbreak that affects many people at ane fourth dimension and can spread through one or several communities
- Pandemic - is the term used to describe an epidemic when the spread is global.
Owned [edit | edit source]

Endemic is derived from Greek en significant in and demos significant people. It is used to describe a disease that is present at an approximately constant level within a order or country. Each state may have a disease that is unique, for example
- Caribbean Dengue is even so nowadays due to a failure to eradicate the Aedes aegypti mosquito (see image R). Dengue offset appeared in the Americas and the Caribbean and with the assist of the Pan American Health Organisation (PAHO) in the 1950s and 1960s the Americas were largely able to eradicate the presence of the Aedes Aegypti virtually eliminating the occurrence of Dengue[two]. However, failure to eradicate its presence in the Caribbean resulted in the continued manual throughout the region and more recently information technology has constitute its fashion back into the Americas causing several epidemics[2].
- Varicella, more commonly known as chickenpox in the United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland. It is more common in children under the age of x, who often but experience balmy symptoms and later exposure develop a natural amnesty to the virus. Although there is a vaccine available information technology is only offered to those who are seen as vulnerable.[3]
- Malaria is another infectious disease that is owned to Africa; through education and implementing countrywide strategies the cases of Malaria are at present falling (see video below)
[iv]
Epidemic [edit | edit source]
An epidemic is derived from Greek epi meaning upon or in a higher place and demos meaning people and is the term used to draw a situation where a disease spreads rapidly to a large number of people in a given population over a curt time period.
The term epidemic is not just used with infectious diseases. It is likewise used with whatsoever scenario that leads to a detrimental rise of wellness risks inside a order. eg.
- The rise in obesity globally (ofttimes described every bit an "obesity epidemic"). Over the concluding 3 decades, the United states has seen an increment in the number of people who accept a BMI college than the recommended average[five].
When the term epidemic is used in connection with infectious diseases it is due to the sudden ascent of cases usually resulting from a new infectious agent or a change in an existing agent, for example:
- An agent moving between host populations, for example moving from animals to humans (zoonotic diseases)[6]
- A genetic change (mutation) in the infectious agent, eg bacteria, virus, fungi or parasite
- Introduction of new pathogens to a host population[7]
Epidemics can follow anticipated patterns and these trends are often used to monitor, predict and command the spread of the infection. A typical example of this is seasonal influenza.
[8]
Pandemic [edit | edit source]
A pandemic is derived from Greek pan pregnant all and demos meaning people and is the term used to draw the rapid spread of a transmissible infectious/communicable disease over several continents or worldwide. Once an epidemic becomes global and affects a large percentage of the population it becomes known as a pandemic. The terms pandemic and epidemic are used to describe the rate and distance of the spread of the disease and not the severity of the illness. Significant features of a pandemic are listed below:
- Affects a wider geographical area, often global
- Infects a very large number of people
- Oftentimes acquired by a new virus or a new strain of a virus that has been fallow for many years.
- Spreads quickly in humans as there is little to no existing immunity
- Tin can crusade a high number of deaths
- Because of the demand to command the spread of the affliction, in that location is frequently social disruption, unrest and economic loss
Escalation of an Epidemic to a Pandemic [edit | edit source]
The World Health Arrangement (WHO) will declare a Pandemic when a disease has shown exponential growth - dramatically increasing charge per unit of growth, each day showing many more cases than the previous solar day. A current example of this is the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). On 31 December 2019, a cluster of cases of pneumonia of unknown cause, in the city of Wuhan, Hubei province in China, was reported to the WHO. This was subsequently identified as a new virus in January 2020 and over the following months, the number of cases continued to rise but were not contained to China and showed exponential growth worldwide. Due to the rapid global rise in cases, this was declared a pandemic on xi March[9] and globally, as of 4:22pm CET, nine December 2020, there have been 67,780,361 confirmed cases of COVID-nineteen, including 1,551,214 deaths, reported to WHO.southward[ten]
Stages of a Pandemic [edit | edit source]
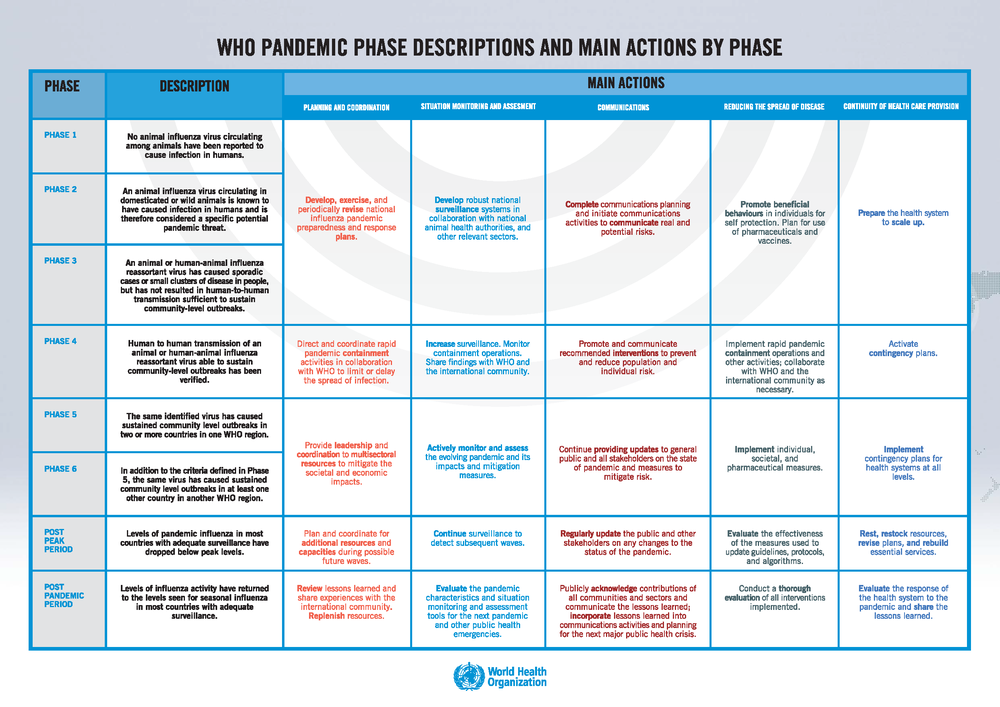
The WHO has identified vi phases that it follows earlier declaring a pandemic[11]. Stage ane represents a low risk and phase 6 is a full-diddled pandemic, you can see the phases below:
- Phase 1 - a virus is seen in animals but has not been shown to infections in humans
- Phase 2 - a known animate being virus has acquired an infection in humans
- Phase 3 - scattered or isolated incidence of cases or small clusters of the illness occurring in humans; possible cases of man-to-homo manual simply non at a level to crusade customs-level outbreaks
- Phase 4 - homo to human transmission at a rate that causes an outbreak in communities
- Phase five - the spread of the illness between humans is now evident in more than ane state
- Phase half dozen - customs-level outbreaks are in at to the lowest degree i additional country other than that seen in phase 5.
Once Phase 6 is reached grooming is then fabricated for a global pandemic. Each phase has a list of actions that demand to exist followed to facilitate transparency and the instruction of wellness organisations and members of the public. The table below describes these actions.
Preventing a Pandemic [edit | edit source]

It is important to try to forbid an epidemic from developing into a pandemic. This requires organisations and nations to act early and exist prepared. A set of policies to try to limit the spread of an infectious agent across the initial individual cases and small-scale clusters of infection are termed Containment. In that location are several measures that have proven effective in the command and containment of viruses[12]:
- Controls - awarding of border controls to limit/forbid movement of individuals to and from affected areas
- Identify cases - brainwash the public on the symptoms and hazard factors, provide easy access to testing, flag potential cases in any healthcare encounters, track contact with infected individuals
- Trace contacts - a labour-intensive process which tracks an infected individual'due south movements from the moment of infection to identify all individuals who have been potentially infected.
- Quarantine - separate an private suspected of infection from contact with others for a certain period of fourth dimension that covers the period of incubation for the disease
- Isolate - dissever an individual who has been identified as infected from contact with others
- Protect - utilise appropriate equipment to protect healthcarew(PPE)orkers who cannot avoid contact with infected individuals.
Summarised by Tomas Pueyo every bit "very apace limit people coming in, identify the sick, immediately isolate them, use heavy protective gear to protect their wellness workers, track all their contacts, quarantine them…" [13]
Managing a Pandemic [edit | edit source]
In one case a pandemic is identified it is vital to accept the appropriate action to contain, manage and reduce the spread of the virus. The key bulletin at this stage is to reduce the manual rate - the number of individuals infected by each single infected individual. If on boilerplate across a population the transmission rate is greater than one the number of cases will continue to increase. Measures that reduce the manual charge per unit to less than one will result in a decline in the full number of infections.
In one case a pregnant level of infection is present within a population then reducing this rate of spread becomes vital. Actions targeted at reducing the transmission rate are termed Mitigation and can involve:
- Social distancing (cancel events, endmost institutions, work from habitation etc.)
- Education of the public - to promote actions such equally paw washing and avoiding groups etc.
- Economic measures - to provide relief to individuals and businesses and to increase compliance with social distancing related policies
All these measures aim to limit the population exposed to infection and to reduce the transmission rate betwixt them. This results in a flattening of the curve of cases over fourth dimension (see figures beneath) and and then reducing the tiptop in the number of cases needing medical care. This maintains the power of the healthcare system to provide quality care to those afflicted and reduce the mortality charge per unit as far as possible. The greater the stress on the healthcare organization the higher the probable mortality rate, as resources are unable to run into the demand and healthcare workers themselves exceed their capacity to provide intendance. Flattening the curve also extends the fourth dimension scale of the epidemic so that whatever potential vaccine can at some future point be used to rapidly increase immunity inside the population.
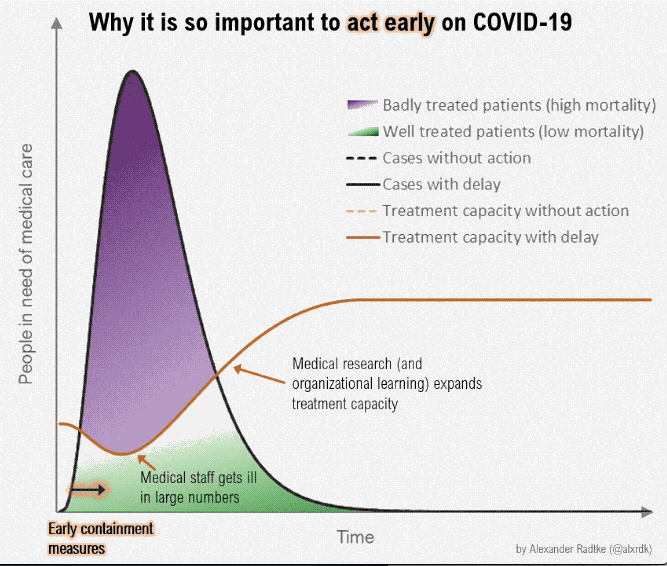
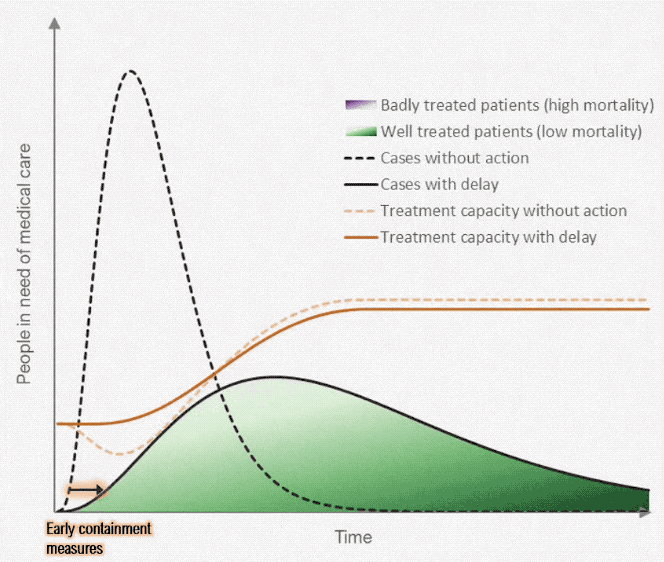
References [edit | edit source]
- ↑ i.0 1.ane The states Department of Wellness and Human Services. Principles of Epidemiology in Public Wellness Practice Third Edition An Introduction to Applied Epidemiology and Biostatistics. Accessed 15 March 2020
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Brandling-Bennett AD, Penheiro F. Infectious diseases in Latin America and the Caribbean area: are they really emerging and increasing?. Emerging infectious diseases. 1996 January;2(one):59.
- ↑ Chickenpox vaccine overview. NHS Website. Accessed 15 March 2020
- ↑ WHO: Global malaria progress and challenges in 2016. Bachelor from:https://youtu.be/x74I-4BZnRo . Accessed fifteen March 2020
- ↑ Mitchell NS, Catenacci VA, Wyatt HR, Hill JO. Obesity: overview of an epidemic. Psychiatric Clinics. 2011 Dec one;34(4):717-32.
- ↑ Engering A, Hogerwerf 50, Slingenbergh J. Pathogen–host–environment interplay and disease emergence. Emerging microbes & infections. 2013 Jan i;ii(1):one-7.
- ↑ National Institutes of Wellness. Understanding emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Biological sciences curriculum study. NIH Curriculum Supplement Series. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD. 2007.
- ↑ Epidemics, Outbreaks and Pandemics. https://youtu.be/CUl87kYHT3I. Accessed on xv March 2020
- ↑ WHO declares the coronavirus outbreak a pandemic. STAT News. Accessed 15 March 2020
- ↑ WHO WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard Bachelor from: https://covid19.who.int/ (last accessed ten.12.2020)
- ↑ Earth Health Organization. Pandemic influenza preparedness and response: a WHO guidance document. Geneva: World Wellness Organization; 2009.
- ↑ Wang CJ, Ng CY, Brook RH. Response to COVID-19 in Taiwan: Large Information Analytics, New Engineering science, and Proactive Testing. JAMA. 2020 Mar 3.
- ↑ Tomas Peuyo, Coronavirus: Why You Must Act Now, Politicians, Community Leaders and Business Leaders: What Should You Do and When?, Medium, March ten 2020 (viewed March 16th 2020) https://medium.com/@tomaspueyo/coronavirus-human action-today-or-people-volition-dice-f4d3d9cd99ca
Source: https://www.physio-pedia.com/Endemics,_Epidemics_and_Pandemics
0 Response to "any infection that spreads from animals to people is referred to by what term?"
Post a Comment